
This will create a list.txt file containing all the zero-byte files found within the current execution folder and all its subdirectories. Highlighted in Red is the DOS name, in Green the Display Name, and in Blue the name as it appears in Explorer. /C 'cmd /c if fsize EQU 0 (if isdir EQU FALSE echo path)' > list.txt. Let’s pause for a moment and take a look at an example. You can then use the old RD command on that name, and remove the folder successfully.
How to delete zero byte files how to#
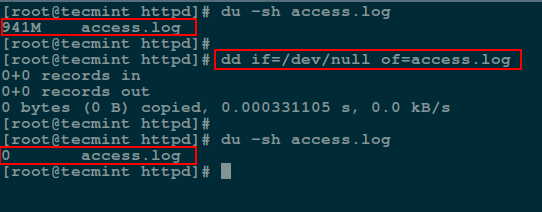
You will find that the old style DOS 8.3 name is used by the system, but a more friendly name is used for display.Īnyway thanks to the wonder of internet Search, i found this great post on how to work around the issue.įrom a CMD prompt you can type in DIR /X and that will show you the actual folder name. I don’t know the reason for it, but it seems that on some occasions, when a user on a MAC creates a folder on an NTFS Formatted share, the name you see, does not actually correspond to the name Windows has for the folder. I was attempting to use robocopy to copy some files from 'Documents' to my backup drive. Secondly, you may even be able to traverse this folder, into folders nested inside it. While GNU sed has no built-in limit on data size, the GNU sed manual explains that system. This might run into a problem if a large disks data exceeds some internal limit of sed. Have you ever had to delete a folder only to find you cant? You check the properties and they are 0 bytes, you cannot check the security tab as you get a message similar to this. If you really want to remove trailing NUL bytes and you have GNU sed, you might try: sed s/x00// /dev/sda >/path/to/sda.stripped.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
